When it comes to the Fed, the default view of many investors often seems to be that high rates are bad and low rates are good, and that the central bank is nearly omnipotent, particularly when it comes to crisis management. While we believe there is some element of truth to these statements, we also think they fall far short of reality and are unhelpful in thinking about the economy and the central bank.
Laissez les bon temps rouler
The financial press tends to portray the current level of Fed rates—around 5.38%—as high, with Fed rate cuts being the key to letting the good times roll. It is true that lower interest rates tend to push the price of assets—such as stocks, bonds, and real estate—higher, as the current value of future cash flows increases in a lower interest rate environment. But this is largely a one-time effect—it’s a shot of adrenaline to securities’ pricing.
This is likely to be excellent news for a short-term or leveraged investor, but for a long-term investor, the difference is largely one of timing. The investment portfolio will likely produce the same or substantially similar lifetime cash flows under either interest rate regime, but low rates lead us to ascribe a higher current value to future gains. And we think that early recognition of future earnings is an absolute negative for investors who are still contributing to their investment portfolios. For any given investment amount, they can buy fewer assets.
There are other mixed impacts to lower interest rates. They can contribute to economic growth and may lead to higher earnings multiples on some assets, but they also reduce reinvestment income on dividends and new investments. We believe these impacts largely cancel out for a typical 60/40 mix of stocks and bonds, although it depends heavily on the underlying assumptions. We think it’s fair to say, however, that the bulk of the perceived positive impact from low rates comes from a one-time pop in asset prices.
Low rates can come at a high cost
The questionable benefits of low interest rates come with real costs. Even a cursory glance at this century’s financial history provides stark reminders of the pitfalls of easy monetary policy.
We think the obvious risk is inflation. The latest iteration of near-zero interest rates was supposed to lead to only “transitory” price impacts; a view that was demonstrably incorrect and has since been abandoned by the Fed. We think inflationary risks are particularly acute when—like now—labor markets and consumer demand are stronger than economic models suggest.
Even more pernicious than inflation, however, is the role of low interest rates on capital allocation. Put simply, when the Fed keeps low risk rates low, investors are forced to take additional—and in many cases unwanted—risks to meet their income needs. The lead-up to the global financial crisis, we believe, is the quintessential example. We have serious doubts if CDO-squareds and subprime mortgages would have sounded attractive to investors had they been able to earn a decent return on lower-risk investments.
It’s the economy—pure and simple
More generally, we believe there’s nothing to fear—and a lot to like—about an economy that can function with higher interest rates. If companies can continue to grow revenues and earnings when rates are high, one of the main implications is that investors can be fairly compensated across the capital structure. Bond holders can earn a decent return on their investment, and shareholders can see growth in earnings and potentially dividends.
Taking a step back, we find it somewhat odd that the Fed is even contemplating rate cuts. The institution is charged with creating full employment, consistent with price stability. We do not see any meaningful indication of labor market weakness, while inflation remains a concern. Not only was the most recent consumer price index report higher than target, but there are also troubling signs of inflation becoming embedded in consumer expectations. The Fed’s preferred measure of this factor—a market derived indicator of annual inflation over a five-year period starting five years in the future—remains stubbornly above target and pre-pandemic levels.
With the economy functioning for workers, companies, and investors, we think a stable Fed policy rate is not a particularly troubling outcome.
Back to the future?
The U.S. economy has previously functioned well at this interest rate level
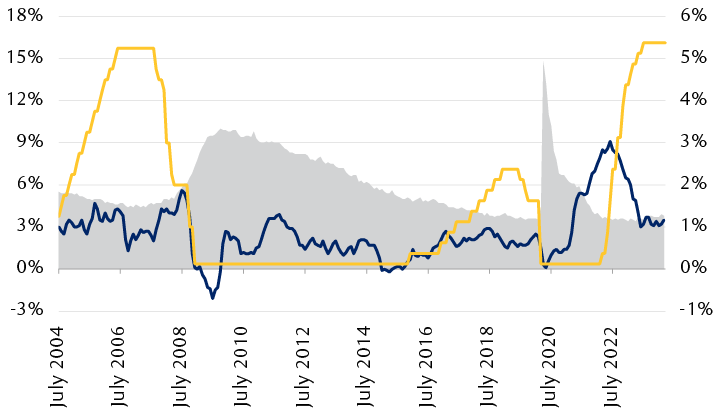
The line chart compares year-over-year U.S. consumer price index inflation, the U.S. unemployment rate, and the Federal Reserve’s overnight interest rate target since July 2004. In 2006 and 2007, when inflation and unemployment were at or near target levels set by the Federal Reserve, the overnight interest rate (5.25%) was similar to today’s (5.375%).
Source - RBC Wealth Management, Bloomberg
Fed omnipotence, well, sort of
The Fed can effectively set short-term interest rates and it has the capacity to fix long-term interest rates—at least for some time. It can also finance any quantity of investments for any length of time. This last power was critical in the bounce back from the global financial crisis as it bought time for assets to recover.
The Fed’s power in a financial crisis was further demonstrated during the regional bank turmoil of March 2023. At the time, we emphasized that the central bank could stop contagion whenever it liked—the issues banks faced then were a quintessential financing issue. Most current active investors, ourselves included, have mainly seen financial crises, leading many of us, we believe, to overemphasize the Fed’s capacity to deal with any economic problem.
The pandemic, however, emphasized the limits of Fed power: the institution has much less impact in the physical world than in the financial world. Supply chain problems are largely outside the Fed’s ability to influence. There’s no level of interest rates that can make a port operate more quickly or make ships sail faster. In theory, the Fed could force interest rates high enough to bring demand in line with reduced supply, but crushing the economy to match a temporary supply reduction is an idea only a theorist could love.
Perils of oversimplification
The Fed is undoubtedly a powerful global institution. In our view, however, the discourse on the central bank too often becomes cheerleading for low rates while emphasizing the Fed’s nearly magical powers. A more nuanced reading of the institution and its policies makes clear that higher rates are not to be feared and that Fed support can only go so far in times of turmoil.
